CPT 49000 - Exploratory Laparotomy (Abdominal Exploration) Guide
What will this article teach you about 49000
CPT Code 49000 describes an exploratory laparotomy, a major abdominal procedure performed when a physician must open the abdomen to diagnose or treat conditions that cannot be confirmed through noninvasive methods. This code applies when the intent is exploration, identification of pathology, or evaluation of trauma, infection, bleeding, or unexplained abdominal findings. In this article, we break down the AMA definition, documentation requirements, common diagnoses, modifier use, bundling rules, payment considerations, and the top reasons claims are denied. This ensures examiners, billers, and surgeons understand how to properly report and review CPT 49000.
The Who, What, When for billing and paying for CPT Code 49000
Definition of CPT Code 49000 - AMA vs Layperson:
The AMA defines CPT 49000 as an “exploratory laparotomy, exploratory celiotomy with or without biopsy.” In practical terms, this procedure involves surgically opening the abdomen to investigate internal organs when imaging alone cannot provide answers. Physicians perform an exploratory laparotomy to determine the cause of severe abdominal pain, trauma, infection, bleeding, or suspected surgical emergencies. In some cases, the surgeon may biopsy tissue during the exploration, but additional therapeutic procedures must be coded separately when appropriate.
When is CPT Code 49000 Used?
CPT 49000 reflects a major surgical procedure used when a physician must explore the abdominal cavity to evaluate conditions such as peritonitis, bowel obstruction, internal bleeding, trauma, suspected malignancy, or complications from previous surgeries. The code is appropriate when exploration is the primary purpose—even if no additional repair or therapeutic intervention occurs. If a definitive surgical procedure is performed, such as bowel resection or repair of organ damage, those services typically replace 49000 unless the exploration was distinct. Claims reviewers look for clear justification that the abdominal exploration was medically necessary and not incidental to another procedure.
Who bills for CPT Code 49000?
General surgeons perform most exploratory laparotomies, particularly in trauma settings or emergency diagnostics. Trauma surgeons, acute care surgeons, and surgical oncologists also bill this code frequently, as do gynecologic surgeons when exploration focuses on abdominal pain or suspected pelvic pathology. Hospitals bill the facility component when the service is performed in the inpatient or outpatient surgical department. CPT 49000 is almost never performed in the office setting and is reserved for fully equipped surgical environments.
Top Diagnosis ICD-10 for CPT 20220
Diagnoses that justify exploratory laparotomy include peritonitis, penetrating abdominal trauma, internal bleeding, bowel obstruction, suspected malignancy, perforation, or undifferentiated abdominal distress that cannot be diagnosed through imaging. ICD-10 codes associated with acute abdomen, trauma, abdominal masses, postoperative complications, and severe infections often appear with CPT 49000. Claims are most frequently denied when the diagnosis suggests a minor condition that does not warrant major exploratory surgery, so linkage between the diagnosis and the surgical necessity must be explicit.
Places of Service for CPT Code 49000
CPT 49000 is performed almost exclusively in operating rooms within hospital inpatient or outpatient settings (POS 21 or POS 22). It is also billed during emergency abdominal surgery performed in trauma centers (POS 23). The procedure requires sterile technique, surgical equipment, anesthesia, and full perioperative support, making office-based billing inappropriate. Claims reviewers look for POS accuracy because reimbursement differs significantly between hospital inpatient and outpatient environments.
Proper Documentation for CPT Code 49000
Thorough, accurate documentation is essential because exploratory laparotomy is often bundled or denied when a more definitive surgical procedure is billed. Surgeons must document the indication for exploration, such as trauma, obstruction, infection, or malignant suspicion. The operative note should describe the incision, the organs and structures examined, any biopsies taken, and the findings that guided intraoperative decisions. If no additional surgical repair is performed, the note must reflect that exploration alone was medically necessary. If additional procedures are performed, documentation must clearly distinguish when the exploration is independent and not incidental.
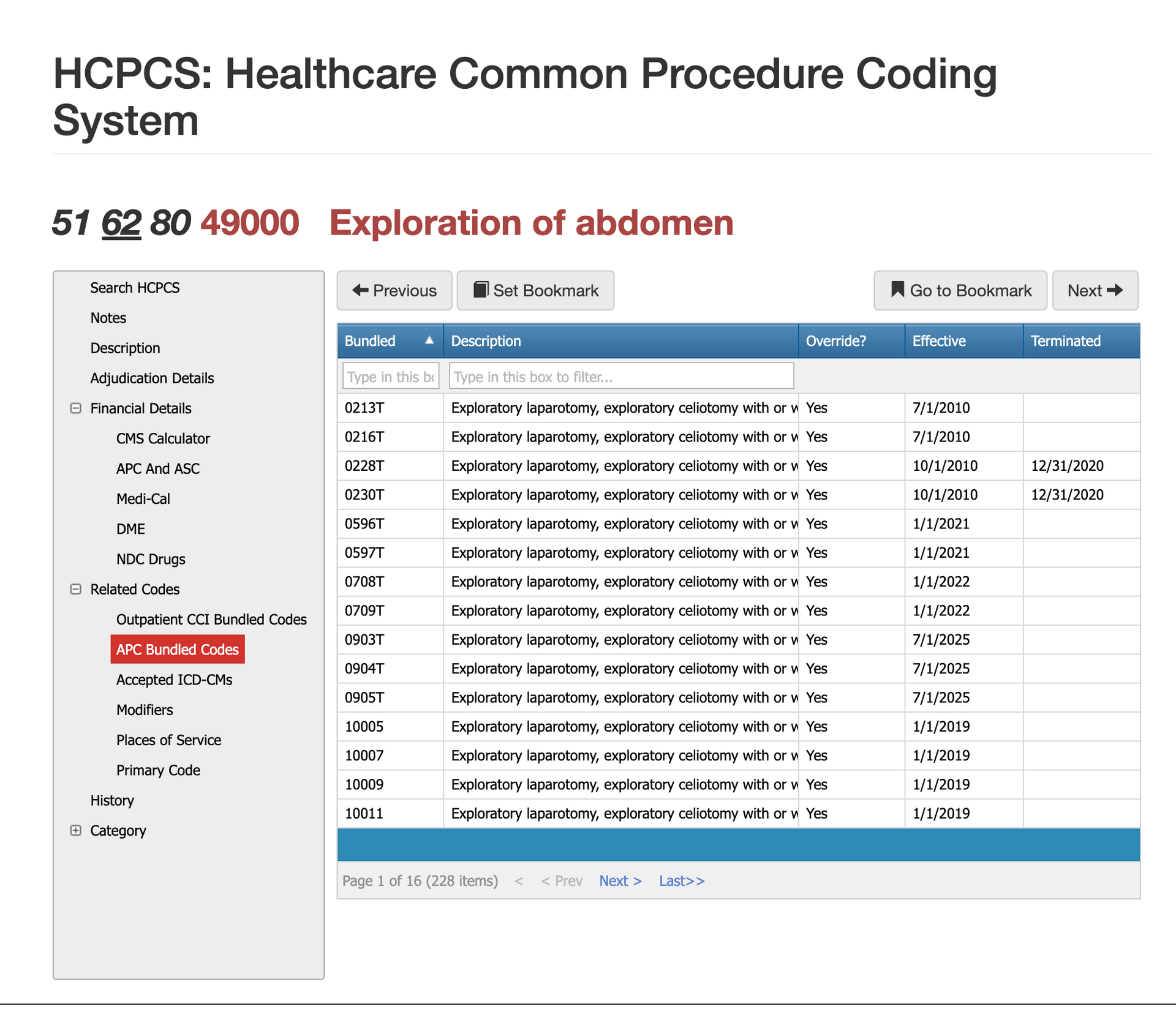
Bundled Codes for CPT Code 49000
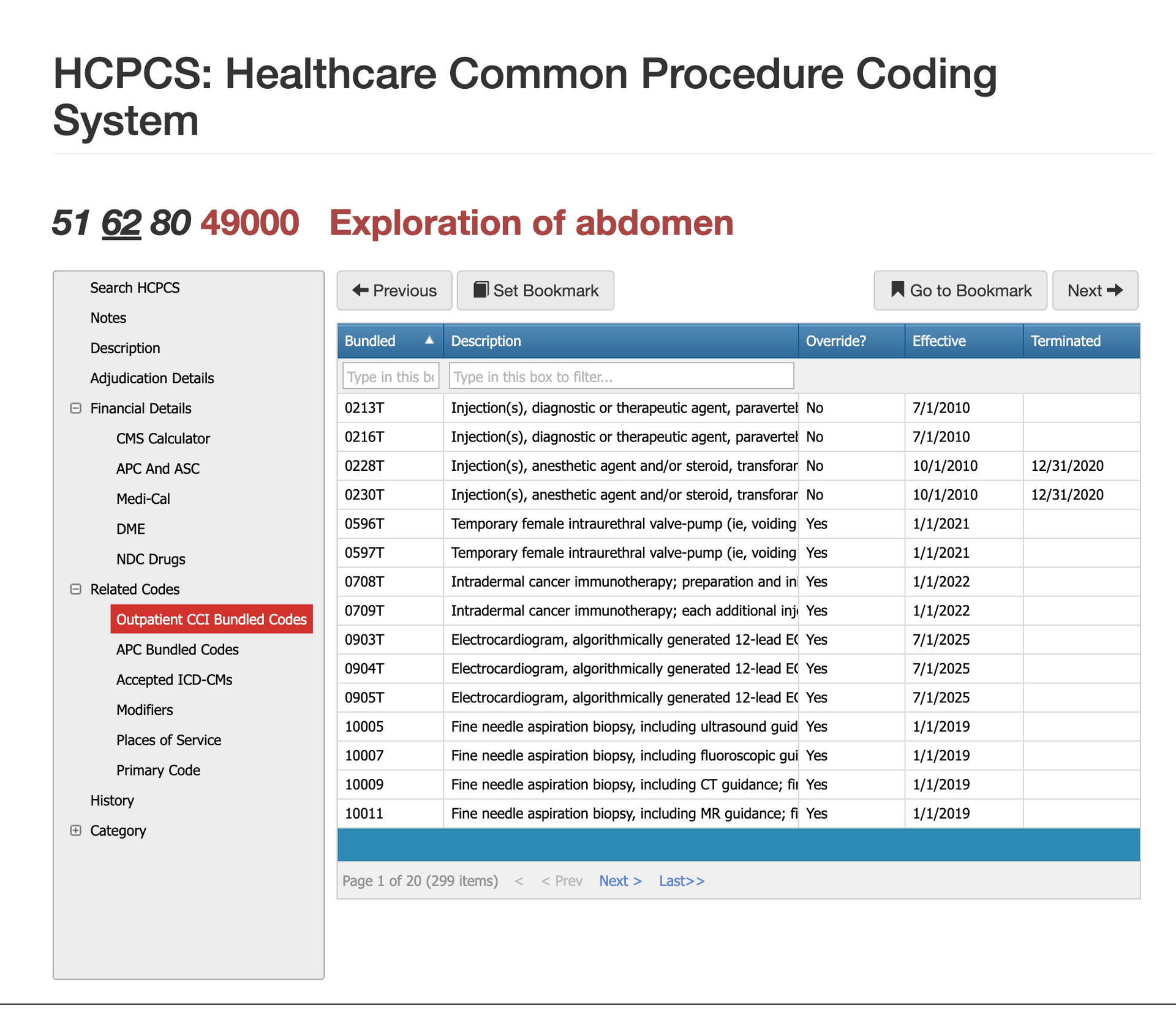
CPT 49000 interacts with several bundling rules because exploration is often integral to other major abdominal procedures. Under CCI edits, 49000 is bundled with most definitive surgeries, including bowel resections, appendectomies, adhesion lysis, and organ repairs. The exploration becomes part of the primary therapeutic service unless documentation supports a distinct reason for exploration unrelated to the main procedure. Imaging guidance is not separately billable because this is an open surgical approach. Claims examiners rely heavily on CCI logic to determine whether 49000 should stand alone or be absorbed by a more complex code, making the operative note critical for adjudication.
Related CPT Codes for 49000
CPT 20220 sits within a family of musculoskeletal biopsy codes that differ primarily by the depth of access, technique, and anatomical complexity. CPT 20225, which represents a deep bone biopsy, is used when the provider must dissect through deeper tissues or when the bone site is not readily accessible by superficial approach. Open surgical biopsy codes in the 20100 series apply when bone must be surgically exposed rather than accessed percutaneously. Imaging guidance codes may also be used when radiologic assistance is documented. Understanding these distinctions is essential because incorrect code selection can lead to significant overpayment or underpayment.
| CPT Code | Descriptor | How It Differs From 49000 | Time Requirement | Key Difference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 49000 | Exploratory laparotomy | Primary code for abdominal exploration without definitive repair. | 10–19 min | Very limited problems; low complexity |
| 44005 | Exploratory laparotomy with lysis of adhesions | More complex, includes therapeutic intervention; replaces 49000 when performed. | 20–29 min | Routine, stable conditions; minimal risk |
| 44120 | Small bowel resection | Therapeutic surgery supersedes 49000. | 30–39 min | Multiple conditions, medication changes, test interpretation |
| 49560 | Repair of incarcerated hernia | Not exploratory; includes repair of pathology. | 40–54 min | Severe issues, significant data review, high-risk decisions |
| 49320 | Diagnostic laparoscopy | Minimally invasive, not an open exploratory laparotomy. | ||
| 44950 | Appendectomy | Definitive therapeutic procedure, bundles 49000 unless exploration was separate. |
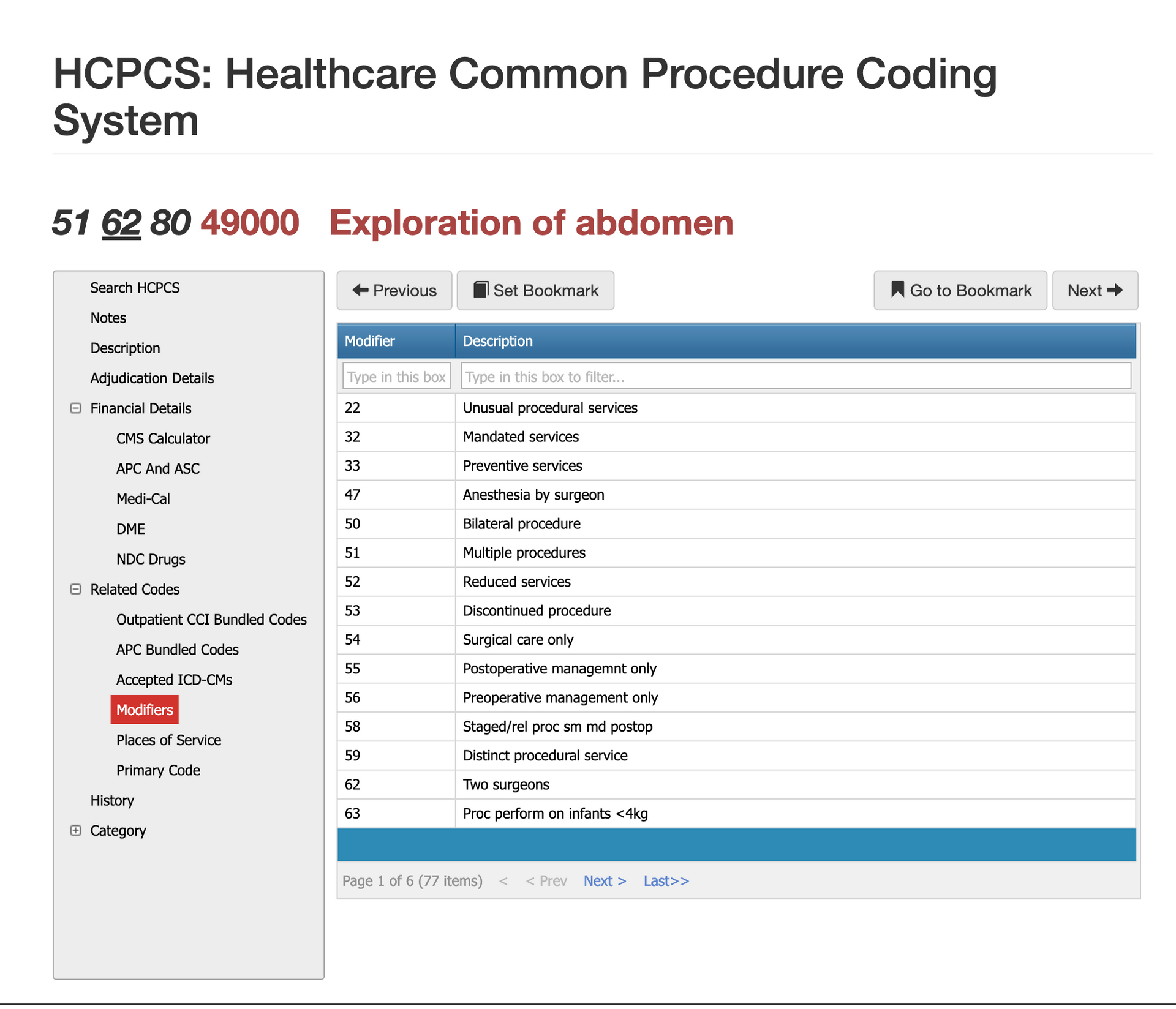
Modifier Guidance for CPT Code 49000
Modifiers help clarify whether CPT 49000 stands alone or is part of a more extensive surgical session. Using the correct modifier prevents denials tied to bundling conflicts or assistant-at-surgery rules.
Modifier 22 for CPT Code 49000
Modifier 22 may apply when the surgeon documents significantly greater work due to extensive adhesions, severe inflammation, distorted anatomy from prior surgeries, or complex trauma. Payers require detailed justification, including time statements and anatomical challenges.
Modifier 51 for CPT Code 49000
This modifier may apply when exploratory laparotomy is performed alongside other unrelated abdominal procedures. However, examiners often deny modifier 51 if the exploration is considered part of the primary procedure, so documentation must clearly separate the intent and complexity.
Modifier 80 for CPT Code 49000
Assistant surgeons are common in major open abdominal procedures. Modifier 80 captures the assistant surgeon’s role, but payers require documentation of medical necessity for a second surgeon.
Most Common Reasons for 49000 CPT Denials
Exploratory laparotomy claims are most frequently denied when documentation does not clearly state why exploration was required, especially when another abdominal procedure was performed. Denials also occur when the diagnosis does not support the need for major abdominal surgery, when billing conflicts with CCI bundling rules, or when payers determine that the service was incidental to a more definitive procedure. Insufficient operative detail—such as failing to describe structures examined or findings discovered—can also trigger medical record requests or downcoding.
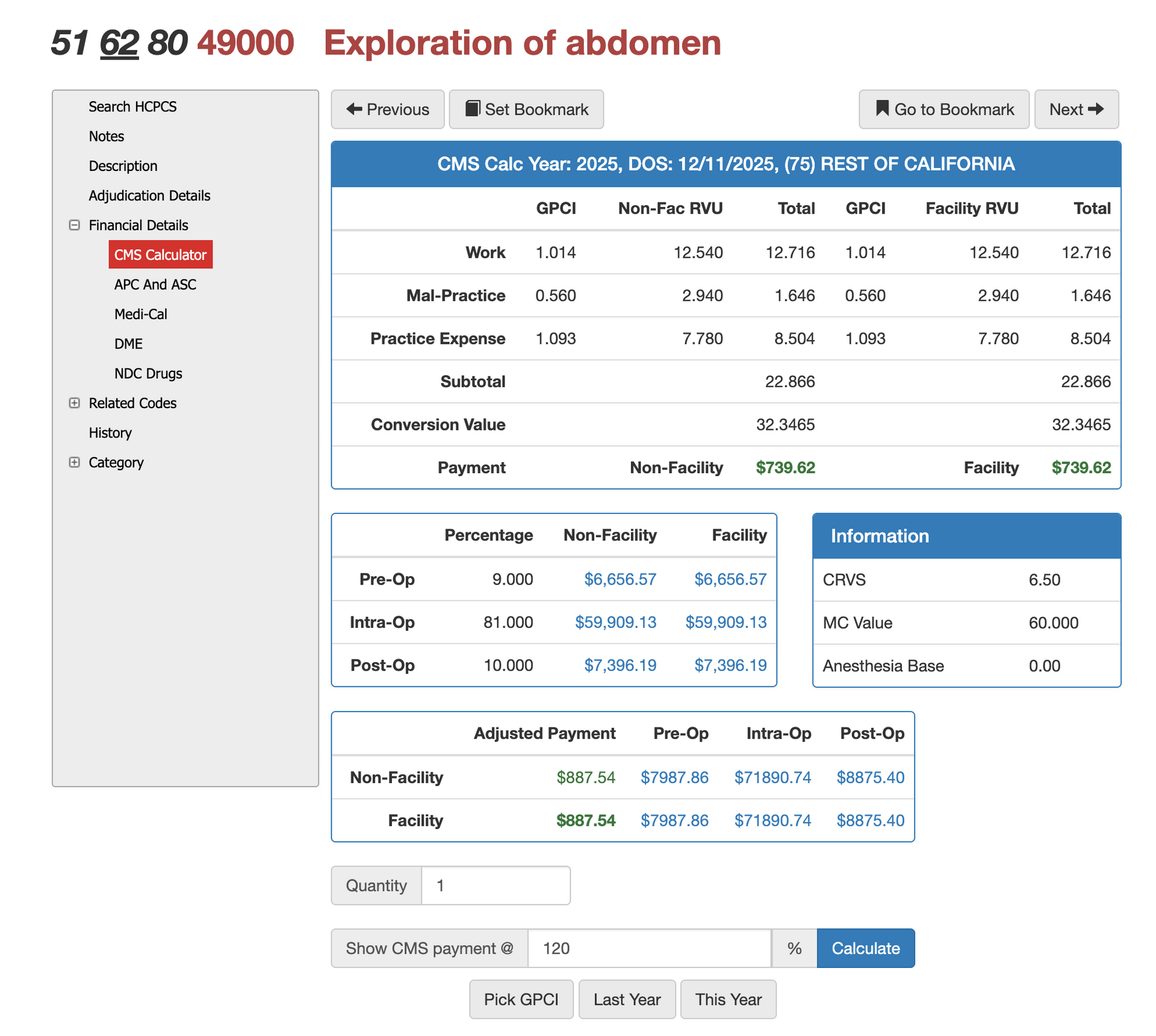
RVUs and Financials for CPT Code 49000
RVU Negotiation Guide for CPT 20220
Reimbursement for CPT 49000 is determined by its RVU structure—work, practice expense, and malpractice components—which vary by region based on the Geographic Practice Cost Index. Because exploratory laparotomy represents a major surgical service with significant physician work and operative risk, the RVU valuation is higher than diagnostic laparoscopy and many other abdominal procedures.
Using Virtual AuthTech or iVECoder allows payers and providers to model reimbursement at various Medicare contract levels, compare facility and non-facility rates, and test out-of-network pricing. These tools ensure contract negotiations align with surgical complexity and that payments remain consistent with CMS guidelines across all service locations.
The Easier Way to Research codes
For more than 30 years, PCG Software has supported Health Plans, MSOs, IPAs, TPAs, and provider organizations in improving coding accuracy, strengthening compliance, and reducing fraud, waste, and abuse. Our solutions, including Virtual Examiner®, VEWS™, and iVECoder®, are built on decades of payer-side adjudication experience and reflect the same logic used by health plans nationwide. National regulatory guidance, payer policies, compliance standards, and large-scale claims review patterns inform this CPT 69210 analysis.
Toss out the CPT book.
Stop researching articles.
Sign up for iVECoder today!
Subscribe
Only get notifications when a new article has been published
Contact Us
We will get back to you as soon as possible.
Please try again later.
About PCG
For over 30 years, PCG Software Inc. has been a leader in AI-powered medical coding solutions, helping Health Plans, MSOs, IPAs, TPAs, and Health Systems save millions annually by reducing costs, fraud, waste, abuse, and improving claims and compliance department efficiencies. Our innovative software solutions include Virtual Examiner® for Payers, VEWS™ for Payers and Billing Software integrations, and iVECoder® for clinics.
Click to share with others