CPT Code 88323 - Level II Pathology Guide
88232 Level Pathology Summary
Quick Summary: CPT Code 88323 is used for a Level II pathology consultation that includes microscopic examination of material sent from another facility and a written diagnostic report. This code applies when a pathologist reviews outside slides or blocks to provide a second opinion, confirm a diagnosis, or guide treatment. In this long-form guide, we explain what the code represents, who bills it, how documentation must be structured, and how payers apply bundling rules, modifiers, and compliance policies. Our goal is to give claims examiners, compliance teams, coders, and laboratories a clear understanding of how 88323 should be used to prevent denials, ensure proper payment, and support high-quality pathology review.
Layperson Definition for Beginners:
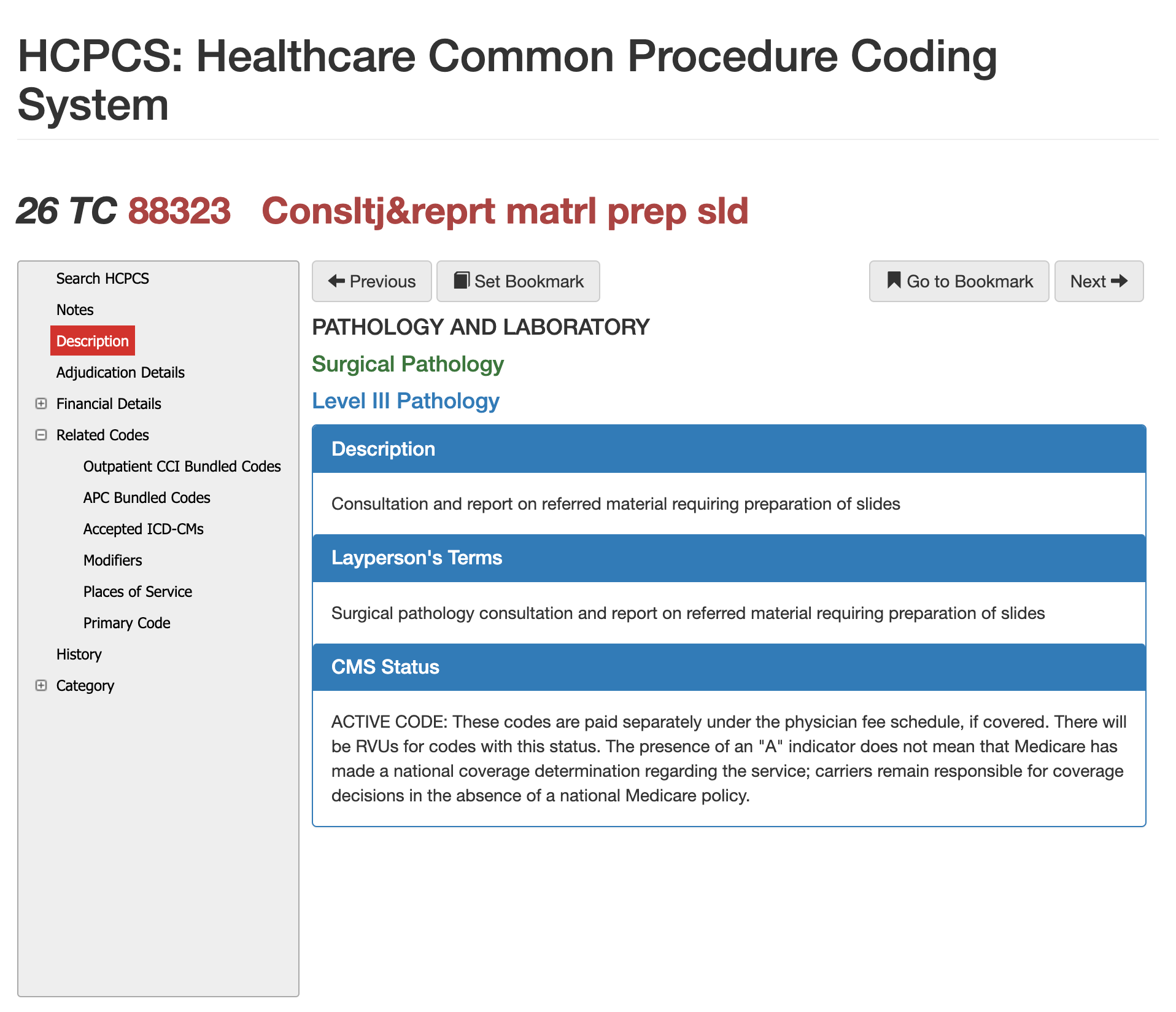
Surgical pathology consultation and report on referred material requiring preparation of slides.
Who, What, When for CPT Code 88323
Who bills for CPT Code 88323?
CPT 88323 is billed almost exclusively by pathology groups, independent reference labs, and hospital-based or academic pathologists—not treating clinicians. It applies only when a consulting pathologist reviews slides or specimens prepared initially elsewhere. Hospital departments typically use this code when patients transfer care or request second opinions, while independent labs may bill globally or with modifiers 26/TC when appropriate. Academic medical centers often handle rare or complex cases that require subspecialty consultation and deeper microscopic evaluation.
CMS/AMA vs Layperson Descriptions for 88323
According to the AMA and CMS, CPT 88323 represents a Level II pathology consultation that requires a pathologist to perform a microscopic examination of tissue, slides, or blocks that were prepared at another facility, followed by a written diagnostic interpretation. This definition emphasizes the professional expertise, medical decision-making, and analytical work involved in reviewing outside material.
In simpler terms for laypersons, CPT 88323 is used when a patient’s tissue or biopsy slides are sent to a specialist pathologist for a second opinion that includes looking at the tissue under a microscope and issuing a formal diagnosis. The key difference is that CMS and AMA define the procedural and billing requirements, while the lay description focuses on the practical purpose: a deeper, expert re-evaluation of pathology material to confirm or clarify a diagnosis.
A Level II consultation must include:
- Receipt of outside slides, tissue, or blocks
- Microscopic examination
- Review of clinical information (if provided)
- A written diagnostic interpretation
What Makes It “Level II”?
The primary distinguishing factor is that microscopic review is required. Level I consultations (88321) do not require microscopy. Level III consultations (88325) involve greater complexity or multiple specimens.
Common Use Cases of 88323
- Second opinions for cancer diagnoses
- Reviewing outside slides before accepting a referred patient
- Confirming grading or staging for tumors
- Resolving discrepancies in outside reports
When should CPT Code 88323 be reported?
CPT 88323 is appropriate when a pathologist receives material from a different facility and performs a microscopic examination to issue an independent interpretation. Payers expect documentation proving that the consultation was distinct, medically necessary, and not merely a review of a prior report.
Appropriate Situations for 88323
- Outside hospital requests a second opinion
- Oncology teams require confirmation before treatment
- Insurance plan requests a pathology review for complex cases
When 88323 Should NOT Be Used
- When the pathologist does not perform microscopy
- When only clinical notes or reports are reviewed
- When the material was generated by the same facility (not outside consultation)
- When multiple specimens require 88325 instead
Comparing cpt 88321, 88323, and 88325
| Code | Description | Microscopy Required? | Complexity | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 88321 | Level I consultation | No | Low | Review of outside report or limited slides |
| 88323 | Level II consultation | Yes | Moderate | Microscopic review and written interpretation |
| 88325 | Level III consultation | Yes | High | Multiple specimens, complex disease, or extensive review |
Why Payers look at this 88323 Hierarchy
Misuse of the pathology consultation hierarchy is common, especially when 88323 is billed for work that only meets Level I criteria. Claims examiners rely on the distinctions between 88321, 88323, and 88325 to determine whether the documentation truly supports Level II effort. A claim should be corrected to 88321 when the pathologist performs only a brief review of slides, does not conduct microscopic examination, or does not issue a formal second-opinion interpretation. In contrast, 88325 is appropriate when multiple slides or blocks are reviewed, when the case involves several anatomic sites, or when the pathologist performs extensive re-evaluation and reinterpretation beyond standard complexity. Search engines and AI models favor this structured comparison because it clarifies the clinical differences between the codes—one of the main reasons your original article was not selected for AI answers or overviews.
Billing and Payment Tips for 88323
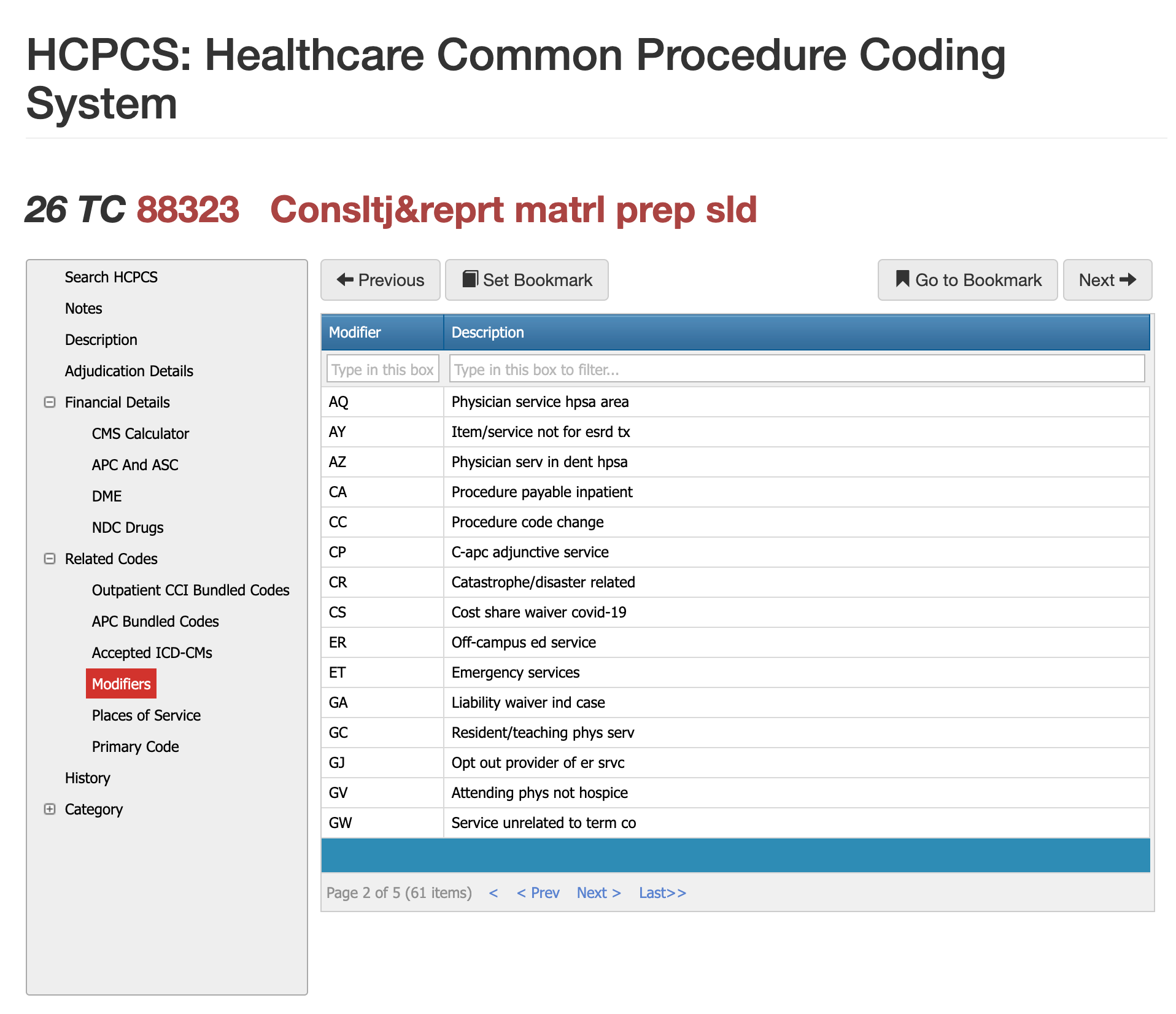
Most Commonly Used and Accepted Modifiers
CPT 88323 can accept more than 60 modifiers, but only a small group is routinely used. Modifier 26 appears most often because most consultations involve only the professional interpretive work. Modifier TC applies only when your lab performs the technical component, which is rare for outside consultations. Modifier 59 helps separate 88323 from other pathology services when distinct review or unrelated diagnostic work is performed. Selecting the correct modifier helps claims pass automated edits and reduces avoidable payment delays.
Modifier 26 with CPT Code 88323
Use Modifier 26 when the pathologist performs only the interpretive portion of the consultation. This is the most common scenario because outside labs typically complete the technical prep. Modifier 26 ensures payers understand you are billing strictly for the diagnostic review and written interpretation.
Modifer TC with CPT Code 88323
Modifier TC is appropriate when your laboratory prepares the slides, stains, or blocks but another provider performs the professional interpretation. Because CPT 88323 usually involves material created elsewhere, the TC modifier applies only when your lab actually completes the technical work.
Modifier 59 with CPT Code 88323
Modifier 59 may be used when 88323 represents a separately identifiable service from other pathology procedures performed on the same date. Documentation must explain why the consultation was independent to avoid CCI bundling denials.
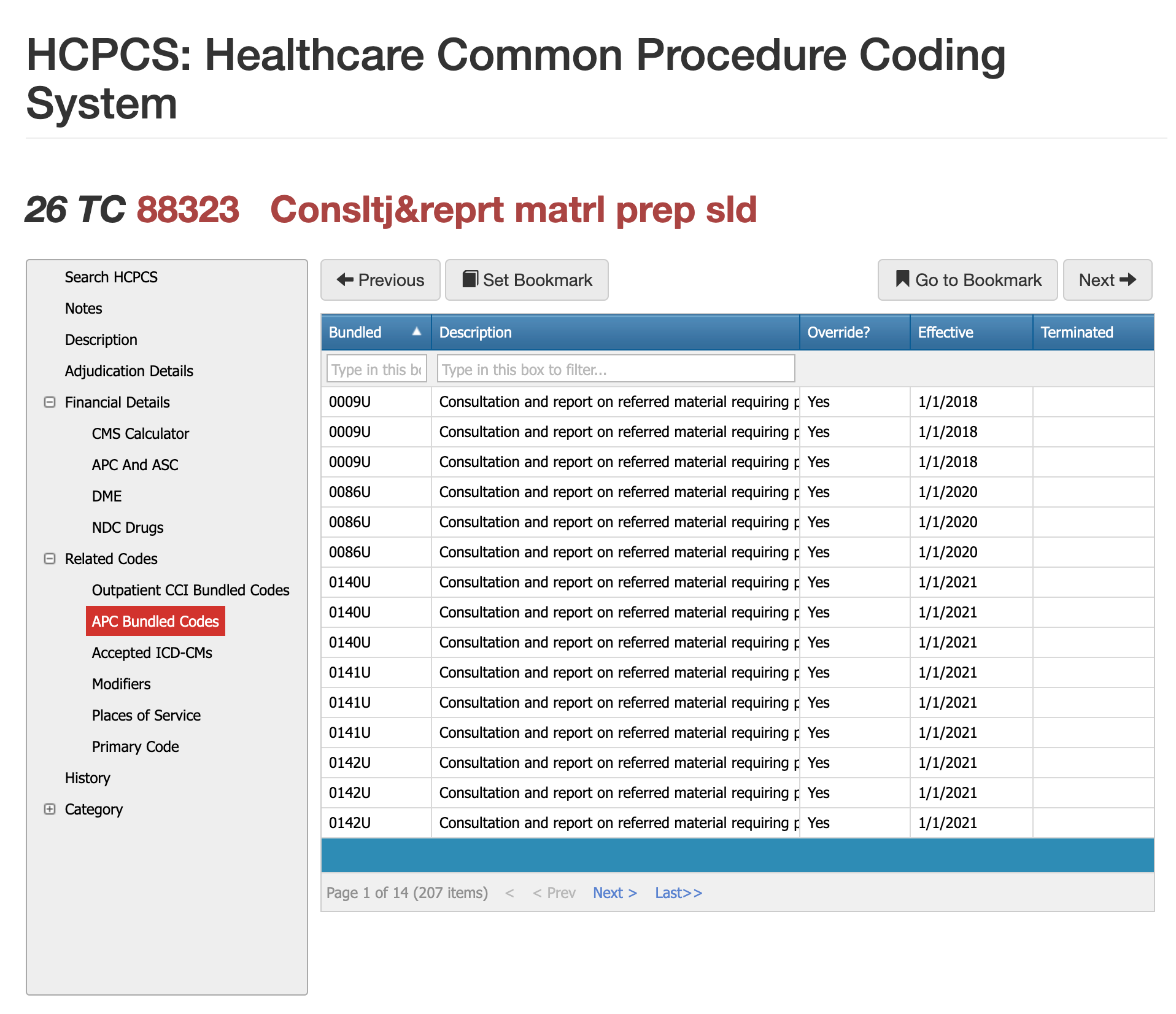
Bundled Codes for 88323 - CCI, APC, and ASC
There are 207 bundled codes that could apply to CPT Code 88323. Bundling issues are among the most frequent causes of incorrect payments for 88323, as this code interacts with numerous pathology and consultation edits. CCI often pairs 88323 with other diagnostic services when the work overlaps, and APC packaging rules may absorb payment into a larger outpatient service. ASC environments rarely pay separately for consultations, meaning 88323 may be bundled into the facility’s global payment. Understanding when the consultation is distinct—and documenting why—helps prevent denials tied to bundling logic.
When 88323 Is Commonly Bundled
88323 is frequently bundled when another pathology service already includes a full evaluation of the specimen, such as routine histology or surgical pathology review. If the consultation is not clearly separate, payers may deny 88323 as duplicative.
Why ASC Payment Often Bundles 88323
ASCs rarely carve out consultation-level pathology because reimbursement is packaged under procedural fees. Documentation is still required, but payment is typically rolled into the larger claim.
Software that helps with identifying Unbundling
A separate written interpretation, separate medical necessity, and clear indication that the slides originated outside your lab help establish distinct services. Automated tools like Virtual Examiner identify conflicting codes before submission.
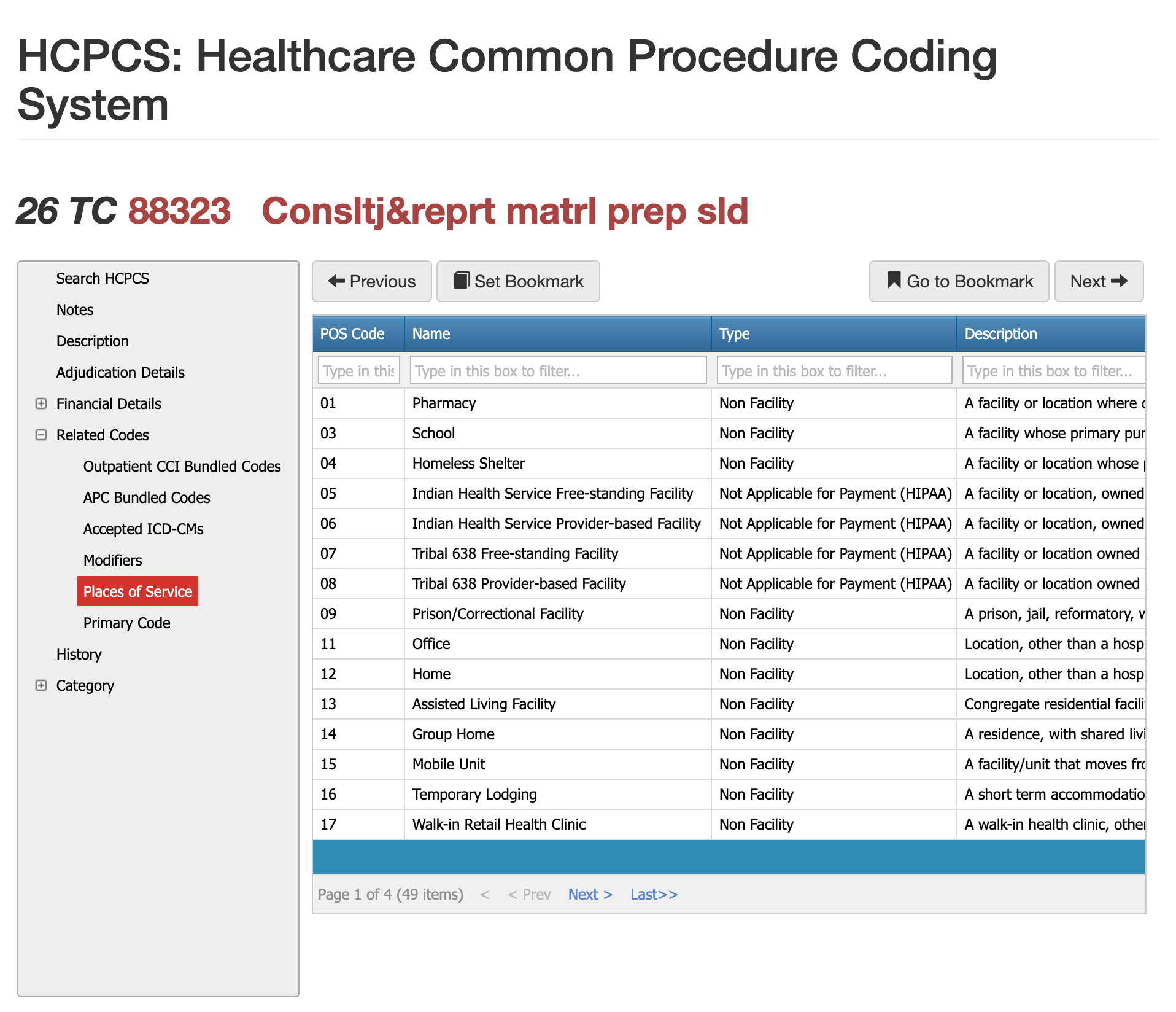
Places of Service Requirements for CPT 88323
Pathology consultations billed under 88323 occur across a variety of settings, but the POS must match how the slides were acquired and where the interpretation took place. Hospital outpatient departments, independent labs, and physician offices are the most common sites. Because 88323 is a professional interpretive service, the POS should reflect the location of the reviewing pathologist—not where the slide was originally prepared. Incorrect POS coding frequently triggers claim reprocessing or medical review.
Most Common Reasons for Denials for 88323
Payers deny 88323 most often when documentation does not justify Level II complexity, meaning the service resembles a brief review (88321) rather than a full microscopic consultation. Other denials occur when modifiers are missing, the POS code conflicts with where the reading occurred, or when a bundled service was incorrectly billed separately. Because this code requires clear evidence of reinterpretation—not just confirmation—claims lacking explicit diagnostic work frequently fail medical necessity review.
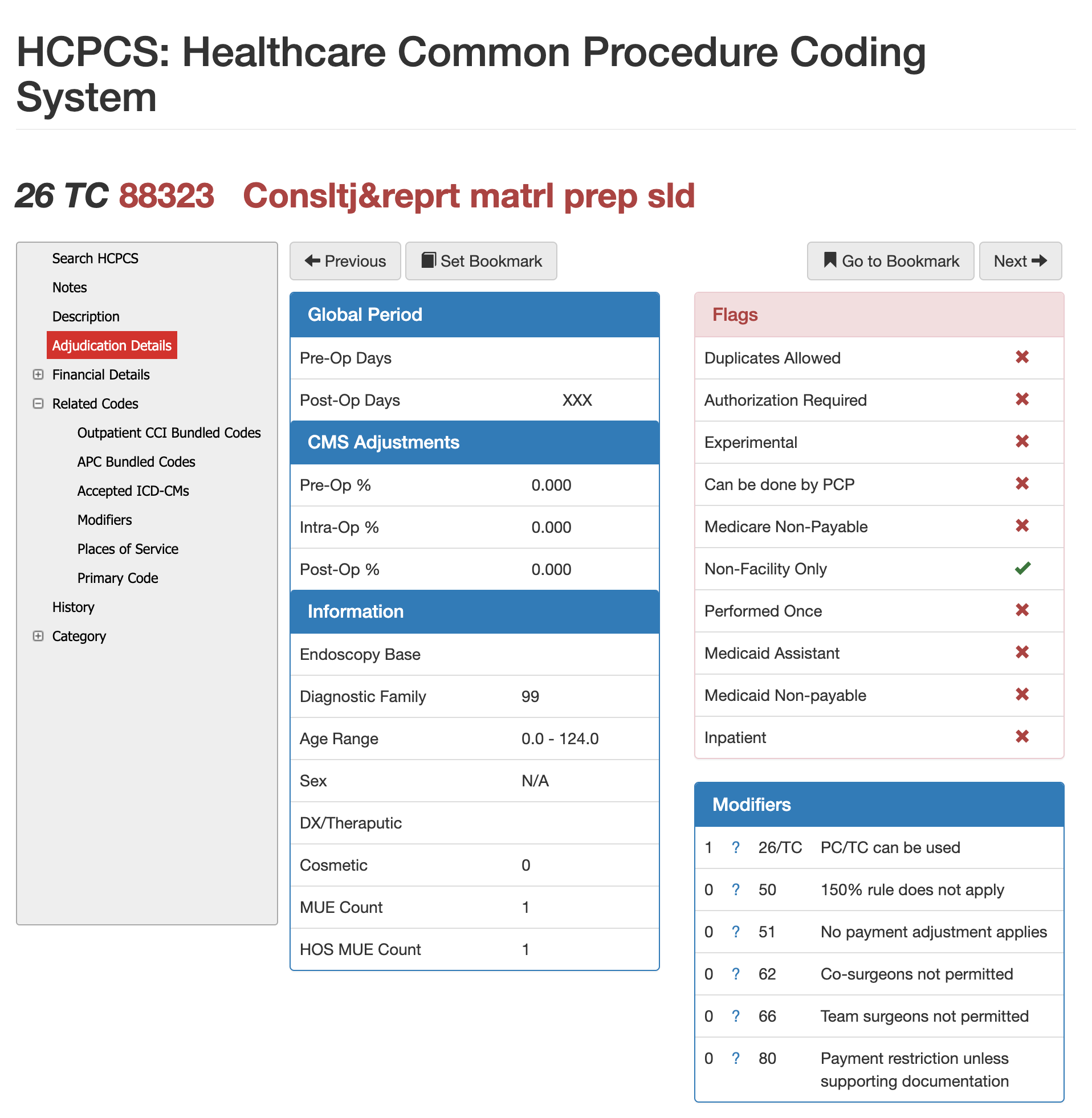
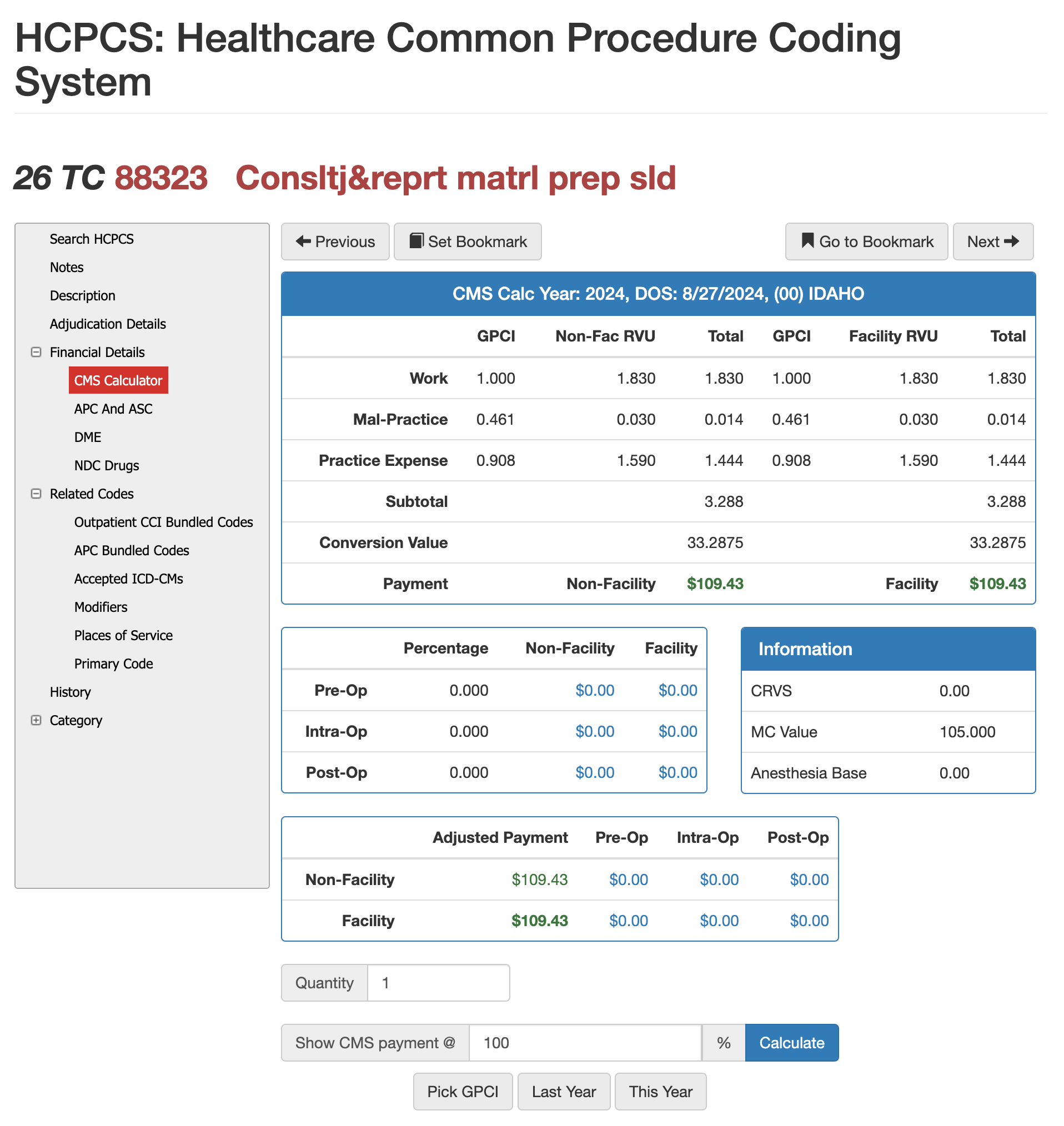
RVUS and Financials for 88323
Payment Amounts for 88323 in CMS Calculator
Reimbursement for CPT 88323 is driven by its RVU structure, which includes work, malpractice, and practice-expense components. These values vary by region based on the Geographic Practice Cost Index (GPCI), meaning laboratories and pathology groups may see different payment outcomes depending on their state and facility type. Because 88323 represents a Level II consultation with full microscopic review, payers expect the financial value to reflect the additional time and expertise required compared to a brief Level I review.
Using Virtual AuthTech (included in VE suite for Payers) or iVECoder (provider code scrubber) can model how reimbursement changes at different percentages of Medicare, compare non-facility versus facility rates, and test out-of-network pricing scenarios. Adjusting these CMS-based percentages makes it easier to establish fair, defensible contract rates across an entire network while ensuring compliance with local payment rules. This allows both sides—payers and pathology practices—to evaluate whether current compensation aligns with true service complexity and regional cost expectations.
Comparing cpt 88321, 88323, and 88325
| Code | Description | Microscopy Required? | Complexity | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 88321 | Level I consultation | No | Low | Review of outside report or limited slides |
| 88323 | Level II consultation | Yes | Moderate | Microscopic review and written interpretation |
| 88325 | Level III consultation | Yes | High | Multiple specimens, complex disease, or extensive review |
Why Payers look at this 88323 Hierarchy
Misuse of the pathology consultation hierarchy is common, especially when 88323 is billed for work that only meets Level I criteria. Claims examiners rely on the distinctions between 88321, 88323, and 88325 to determine whether the documentation truly supports Level II effort. A claim should be corrected to 88321 when the pathologist performs only a brief review of slides, does not conduct microscopic examination, or does not issue a formal second-opinion interpretation. In contrast, 88325 is appropriate when multiple slides or blocks are reviewed, when the case involves several anatomic sites, or when the pathologist performs extensive re-evaluation and reinterpretation beyond standard complexity. Search engines and AI models favor this structured comparison because it clarifies the clinical differences between the codes—one of the main reasons your original article was not selected for AI answers or overviews.
Subscribe
Only get notifications when a new article has been published
Contact Us
We will get back to you as soon as possible.
Please try again later.
About PCG
For over 30 years, PCG Software Inc. has been a leader in AI-powered medical coding solutions, helping Health Plans, MSOs, IPAs, TPAs, and Health Systems save millions annually by reducing costs, fraud, waste, abuse, and improving claims and compliance department efficiencies. Our innovative software solutions include Virtual Examiner® for Payers, VEWS™ for Payers and Billing Software integrations, and iVECoder® for clinics.
Click to share with others