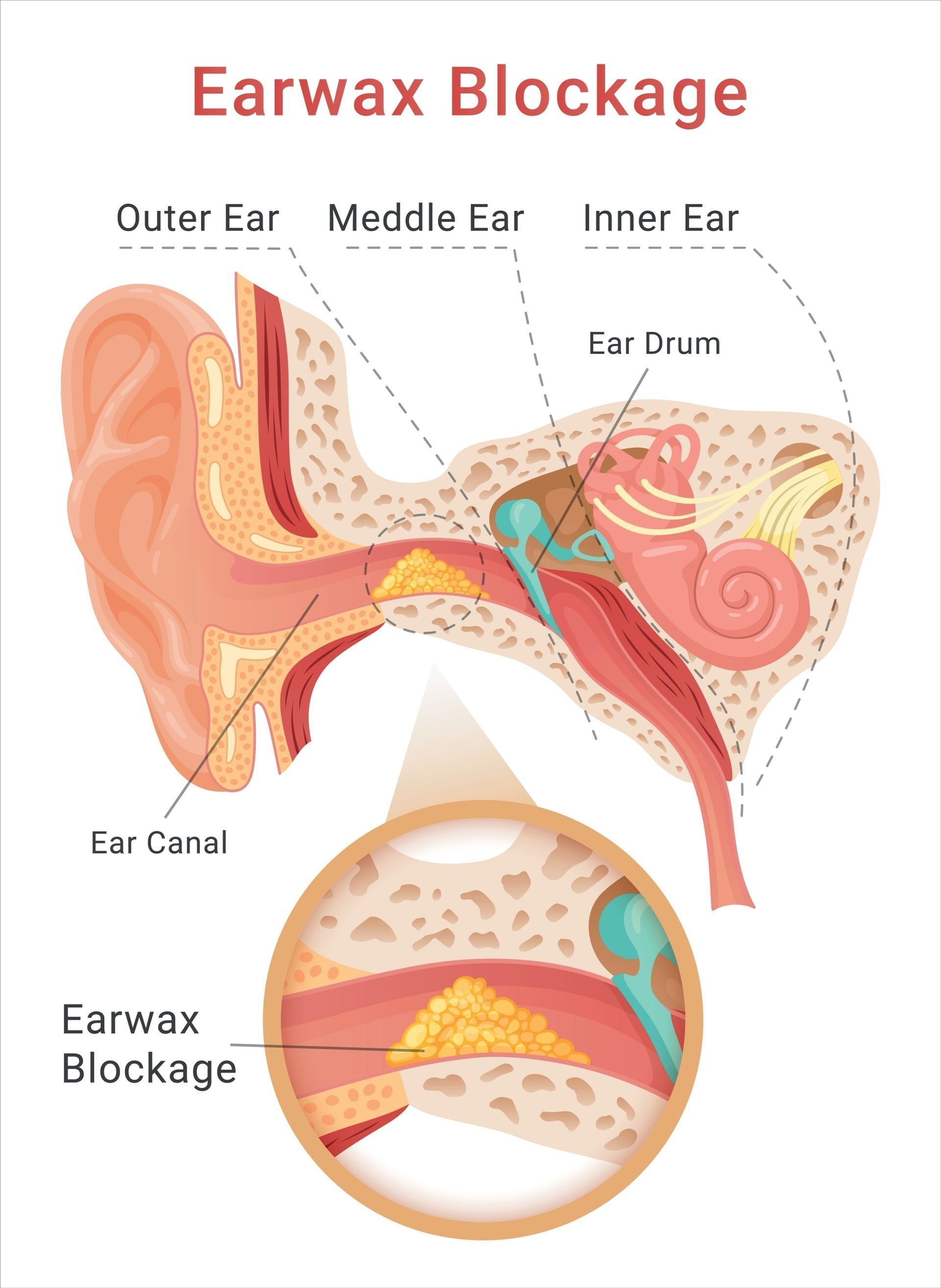
CPT Codes 69210 Defined and Usage Scenarios
62910 Earwax Blockage, Impacted
Summary:
CPT 69210 is used when impacted cerumen (earwax) must be removed
with instrumentation, not irrigation alone. The code is
inherently unilateral, requires documentation showing
true impaction, and must demonstrate that the provider used
tools such as curettes, loops, forceps, or suction to remove wax that could not be cleared by simple lavage. Impacted cerumen must be clinically significant—obstructing the canal, impairing exam of the tympanic membrane, causing symptoms, or requiring physician-level skill for safe removal. Documentation must clearly support
medical necessity,
method of removal, and
laterality.
69210 CPT Code General Information
When is CPT 69210 reported?
Tightly packed or obstructive materials hinder complete visualization of the ear canal or tympanic membrane, leading to symptoms such as pain, hearing loss, itching, dizziness, tinnitus, or infection. If the buildup is too complex, dry, or excessive to be removed without magnification and the expertise of a physician, it cannot be cleared solely by irrigation or lavage; the essential factor is the need for instrumentation. When irrigation is the sole method employed, the appropriate code is CPT 69209.
Layperson Definition for Teaching Purposes: Removal of impacted earwax.
CMS Status: These codes are reimbursed separately under the physician fee schedule, provided they are covered. They will also have assigned RVUs. The "A" indicator does not indicate a national coverage decision by Medicare; local carriers are still responsible for making coverage determinations when no national policy exists.
Doctors who bill for CPT Code 69210
CPT 69210 is billed across a wide range of medical specialties because impacted cerumen occurs in patients of all ages and often presents in both routine and urgent settings. Primary care physicians, family medicine providers, pediatricians, internists, and geriatric specialists frequently report this code during evaluations where ear obstruction interferes with examination or causes symptoms. Otolaryngologists (ENT specialists) are among the most common users of 69210, particularly when removal requires magnification, suction, or specialized tools. Emergency medicine providers and urgent care clinicians also bill this service when patients present with acute pain, hearing loss, dizziness, or infection. In institutional environments, hospitalists and skilled nursing facility physicians may perform the procedure for residents who cannot self-manage impaction. Certain advanced practice clinicians—including nurse practitioners and physician assistants—may report 69210 when allowed under state scope-of-practice rules and payer policies. While audiologists often encounter cerumen during testing, Medicare prohibits them from billing 69210, and many commercial payers require alternative HCPCS coding when the service is performed by an audiologist.
Clinical Documentation and Denial Reasons for 69210
CPT 69210 is defined as a unilateral service, and therefore applies to only one ear. Bilateral treatment may require modifier 50 or RT/LT pairs, depending on payer rules. Irrigation alone cannot be billed under 69210; such services must instead be coded as 69209. Cerumen is considered impacted when it obstructs the ear canal or tympanic membrane, causes symptoms, or requires instrumentation for removal. An E/M service may be reported on the same day only when the provider documents a separately identifiable evaluation beyond the procedure itself, and the E/M is medically necessary. ICD-10 codes H61.21, H61.22, and H61.23 are commonly associated with claims for impacted cerumen, depending on laterality. Audiologists cannot report 69210 for Medicare beneficiaries, and some payers require G0268 instead.
Why is 69210 Approved then Denied from Claims Teams?
Auditors and automated claims engines often flag CPT 69210 when the documentation suggests that simple irrigation was performed, when instrumentation is not clearly described, or when bilateral claims do not align with payer policy. Additional flags occur when E/M coding is unsupported, when the service is paired with procedures that bundle under NCCI edits, or when the claim exceeds the MUE limit. Claims may also be flagged when audiologists report 69210 for Medicare patients or when diagnosis coding does not meet the clinical definition of impaction. These are key indicators of improper billing and frequently lead to denials, recoupments, or post-payment review.
Instrumentation Requirements for CPT 69210
For proper reporting of 69210, the use of instrumentation must be explicitly stated. In this context, “instrumentation” means the use of an otoscope and a physical instrument, such as a curette, wire loop, suction device, right-angle hook, or similar tool, designed for controlled wax extraction. When irrigation or lavage is the only method employed, CPT 69210 may not be used. Instead, irrigation-only removal is reported with CPT 69209. This distinction remains one of the most scrutinized elements during payer review, claim audits, and compliance investigations.
Documentation should always indicate that cerumen was impacted, describe the method of removal, specify the tools used, confirm laterality, and state the clinical reason the removal was required. If the purpose of the visit involved preparation for another medically necessary diagnostic test, such as audiology, that should also be included.
Unilateral Coding, Bilateral Considerations, and Payer Variability
CPT 69210 is defined as a unilateral procedure. When impacted cerumen is removed from both ears, many commercial payers require modifier 50 to indicate a bilateral service. However, Medicare’s historical interpretation has differed. In certain years, some Medicare Administrative Contractors have not recognized modifier 50 for this service and have denied bilateral submissions entirely, paying for neither ear. Private payers are inconsistent: some follow Medicare’s logic, while others permit bilateral billing. Because of this variability, clinicians and billers should confirm payer-specific rules before submitting bilateral claims. In every case, the documentation must separately describe the work performed on each ear.
E/M Code May Be Reported with 69210
An Evaluation and Management (E/M) service may be billed on the same date as 69210 only when the visit meets the criteria for a significant and separately identifiable evaluation. To qualify, the reason for the visit must be distinct from the cerumen removal itself. The provider must also document that an otoscopic examination was initially impossible due to impaction, that the removal required direct provider skill, and that the E/M elements were carried out independently of the procedure. When these conditions are met, modifier 25 is appended to the E/M code. Failure to document the separation between the two services is one of the most common triggers for denials and payer audits.
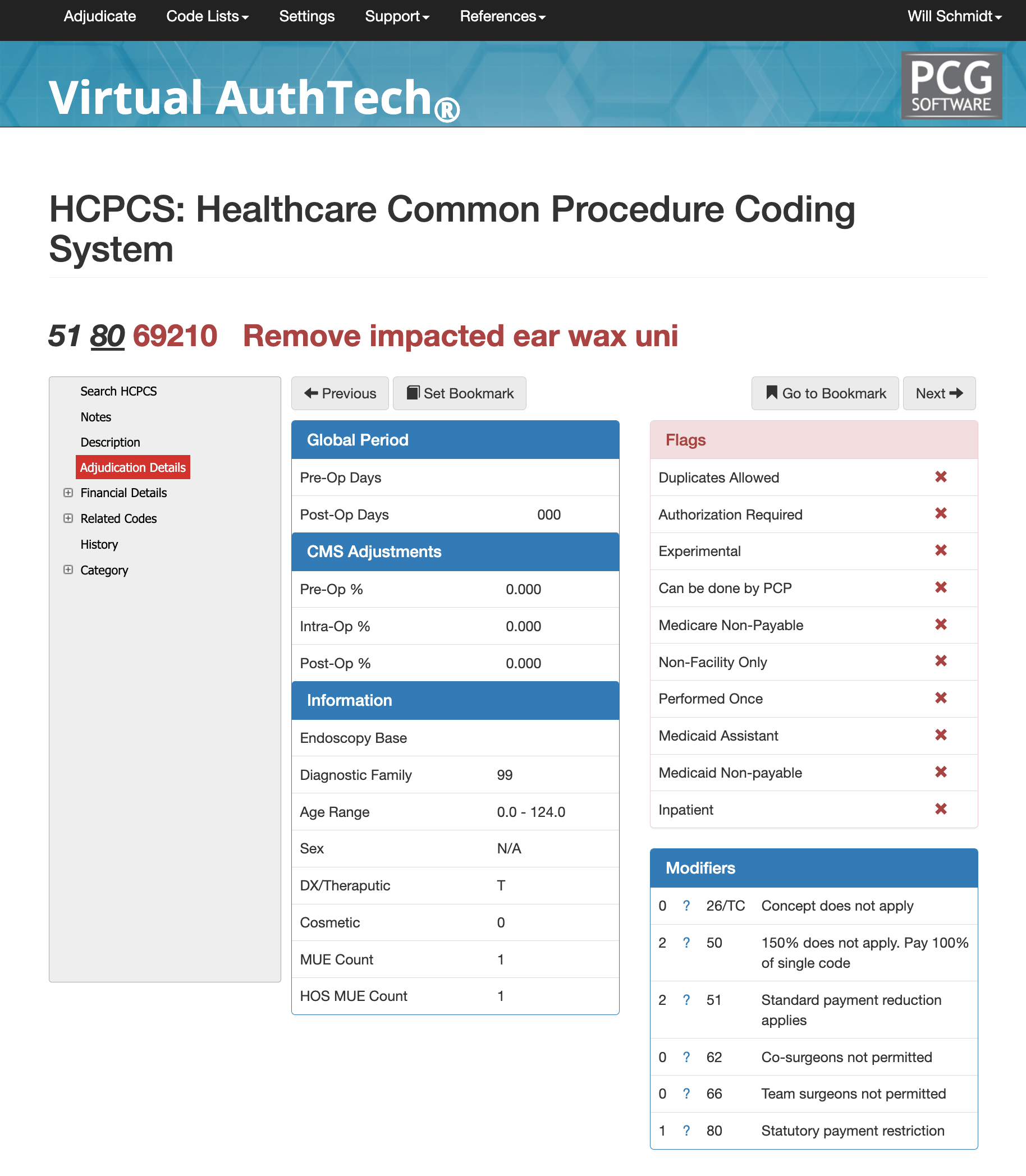
Microscopy, Add-On codes, 69210 and 92504
Add-on code +69990, which describes microsurgical techniques requiring an operating microscope, cannot be billed in conjunction with 69210. The use of the microscope alone does not qualify. However, CPT code 92504, which describes binocular microscopy as a separate diagnostic procedure, may be reported in addition to 69210 when the microscope is used for visualization and when the payer permits it. Even though 69210’s descriptor no longer includes the microscope, many payers still bundle 92504 with cerumen removal. As always, payer policy supersedes CPT guidance.
Adjudication, RVUs, and Payment for CPT Code 69210
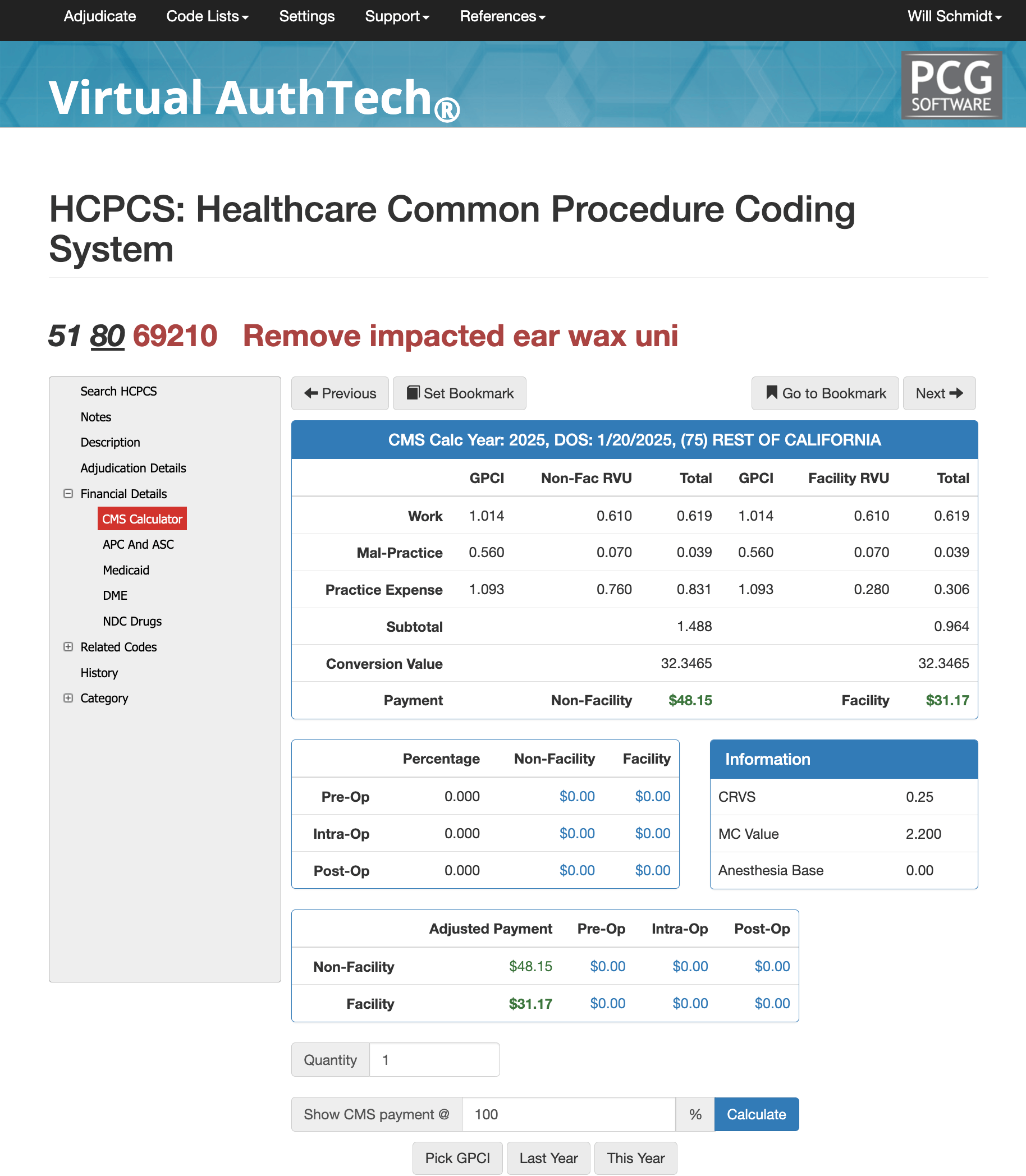
RVU and Payments for 69210
From an adjudication perspective, CPT 69210 carries zero pre-operative and post-operative global days and is considered a standalone minor procedure. Claims may be processed under Diagnostic Family 99 and are appropriate for patients across all standard age ranges. Medicare assigns an MUE (Medically Unlikely Edit) of 1 for this service, meaning only one unit per date of service is typically allowed. RVU values vary by region due to the Geographic Practice Cost Index (GPCI). For example, a California GPCI illustration may show work RVUs of 0.61, malpractice RVUs of 0.07, and non-facility practice expense RVUs near 0.760, with lower facility practice expense values. Software such as Virtual AuthTech allows payers and clinics to adjust contract percentages and examine how reimbursement changes when applying different Medicare-based payment models.
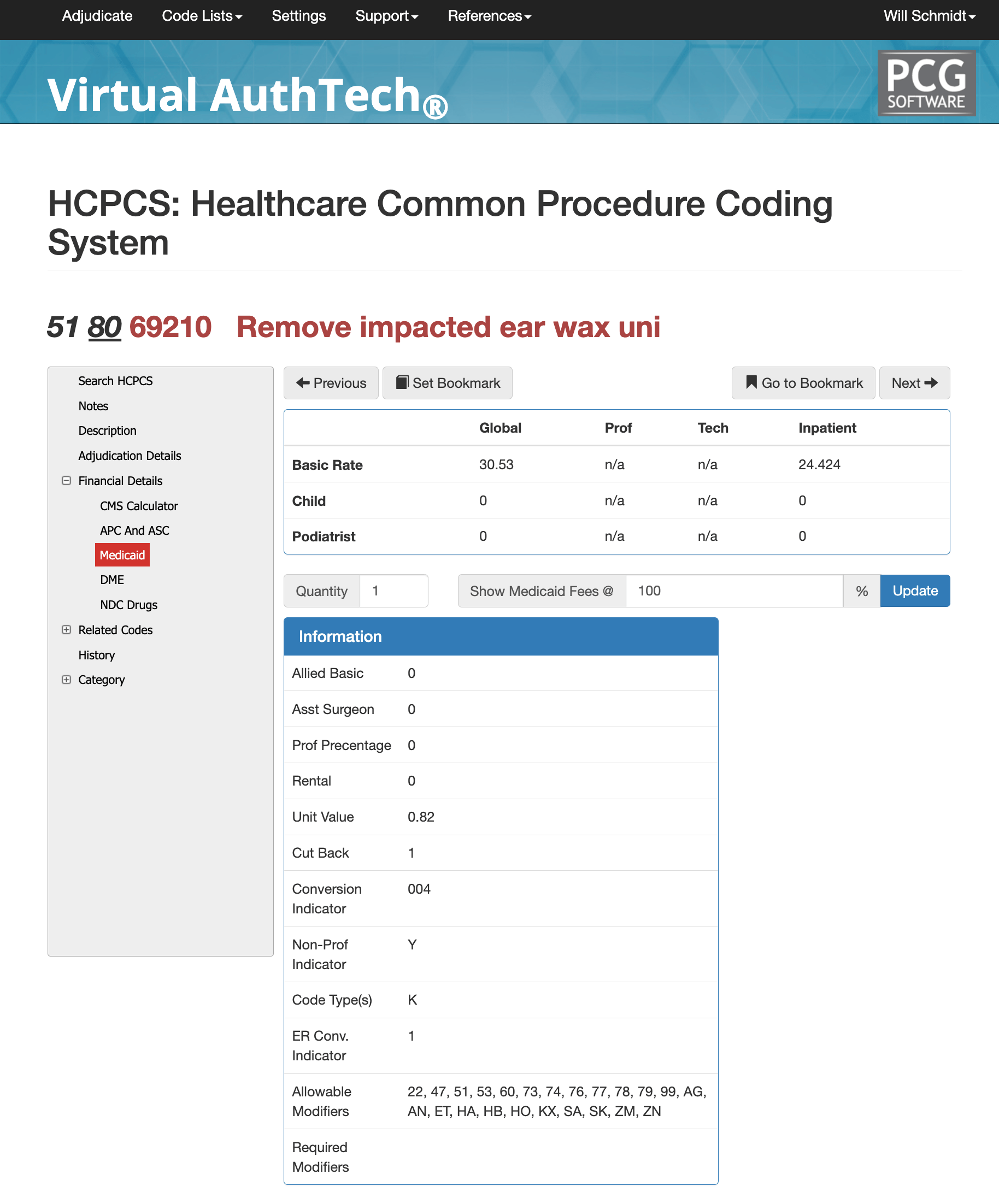
APC, ASC, and Medicaid Consideration for 69210
In the hospital outpatient setting, CPT 69210 is grouped into APC 05733, classified as a Level 3 Minor Procedure. It is assigned a Q1 status indicator and reimbursed under the applicable OPPS payment methodology. By contrast, in Ambulatory Surgery Centers (ASCs), the service carries an N1 indicator, meaning payment is packaged and no separate ASC reimbursement is issued for this code. Medicaid programs differ significantly by state. For example, California’s Medi-Cal reimbursement structure assigns unique global and inpatient values for this code. Providers should rely on state-specific Medicaid fee schedules or payer tools such as Virtual AuthTech for exact rates.
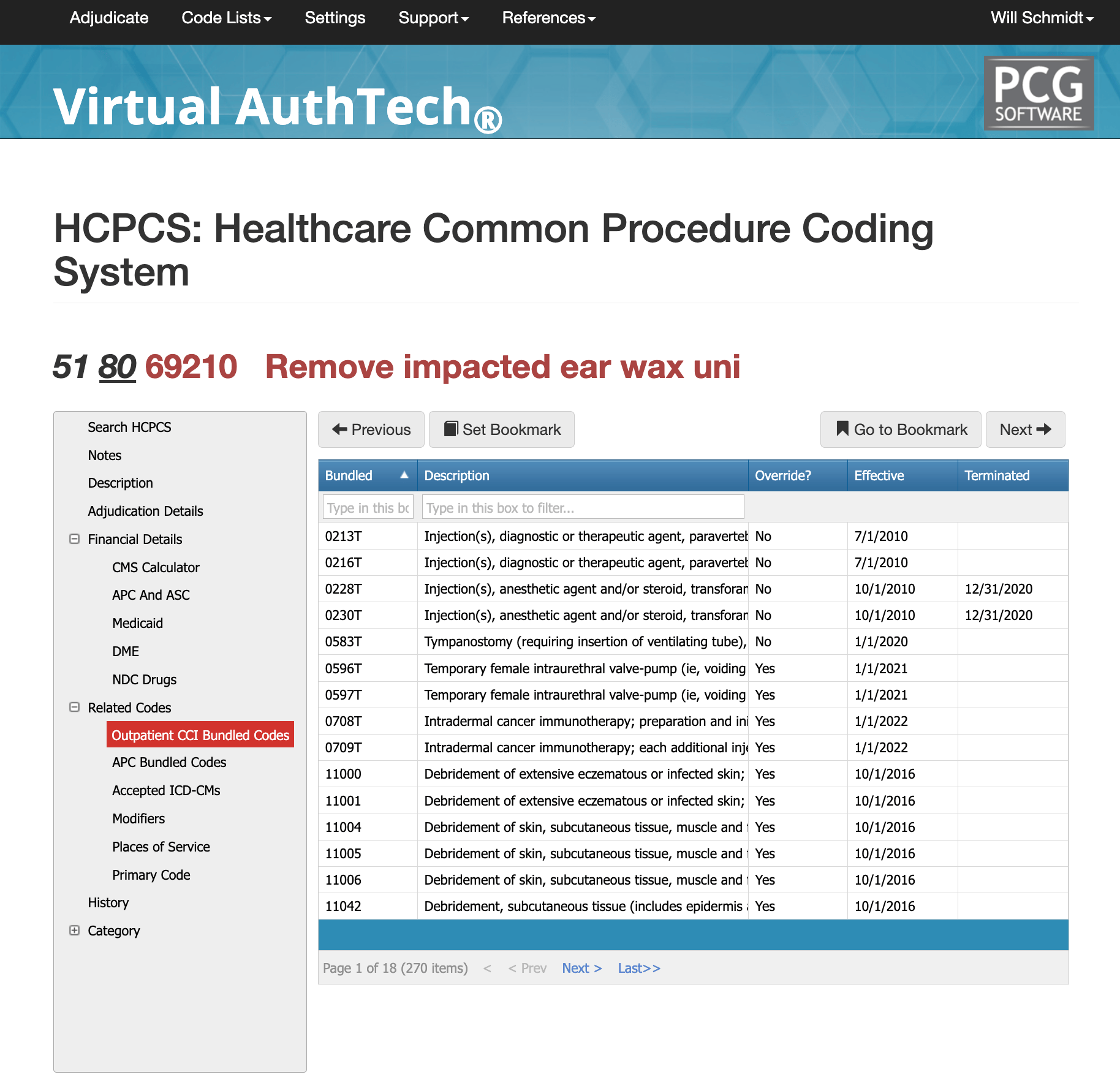
CCI Bundled Codes and Edits for cpt code 69210
CPT 69210 is involved in thousands of potential CCI edit pairings, reflecting how frequently it appears alongside other ENT, primary care, or urgent care services. In many situations, cerumen removal is considered incidental or bundled into other procedures unless the documentation proves separate necessity. Common denials arise when the record does not demonstrate true impaction, when irrigation rather than instrumentation was used, when laterality is unclear, or when a bilateral claim is submitted to a payer that prohibits modifier 50. Additionally, E/M services are often denied when modifier 25 is missing or unsupported. Running a mock adjudication through a coding engine helps identify bundling conflicts before submission.
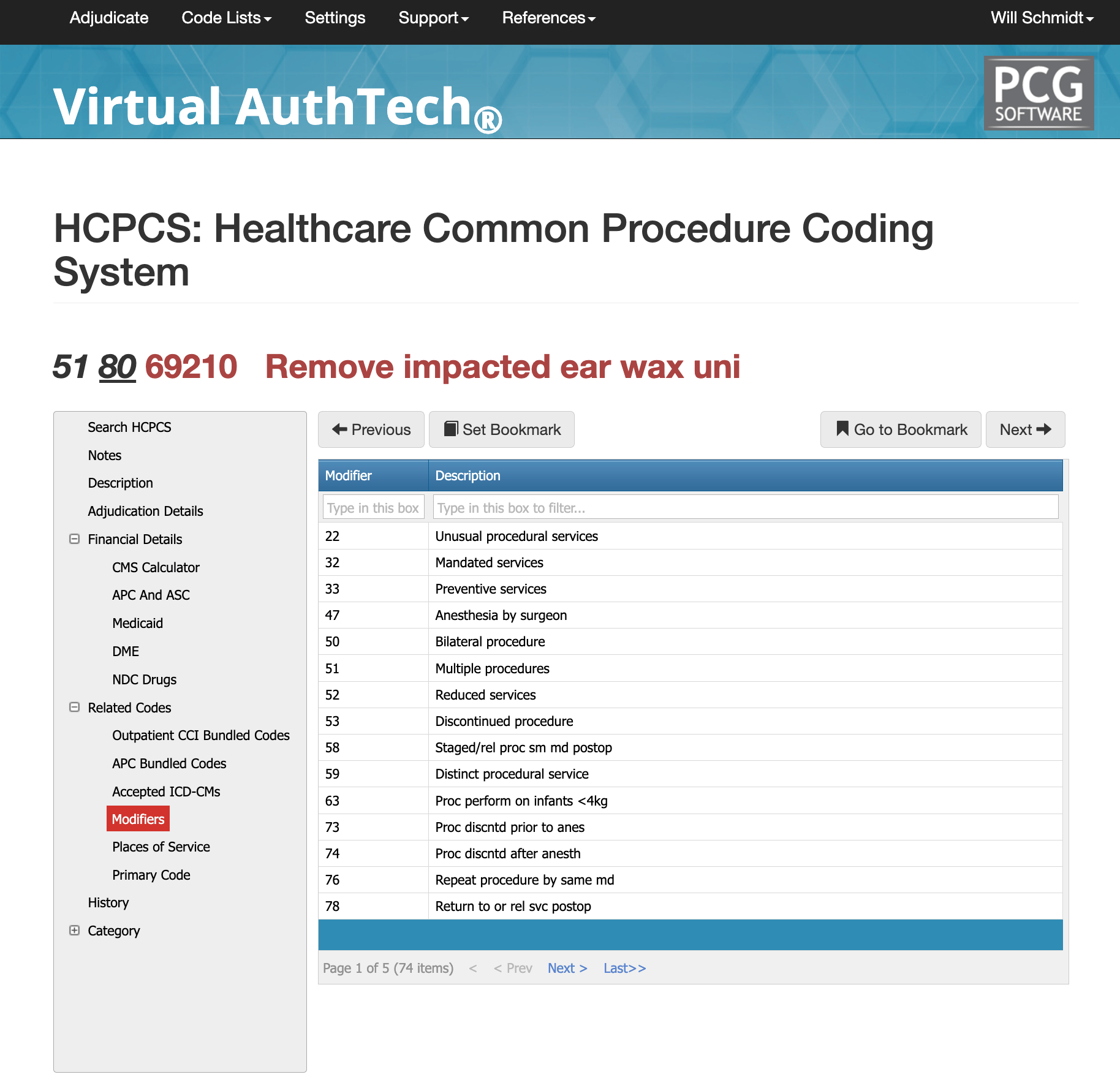
Most Common Modifiers of CPT Code 69210
The usage for 69210 must align with both the documentation and the payer policy. Modifier 50 is often used for bilateral removal if permitted by the payer, while RT and LT may be used to denote the specific ear treated. Modifier 25 is appended to an E/M code when the evaluation is separate from the procedure and fully supported by documentation. Modifier 59 may be appropriate when 69210 must be reported as distinct from another procedure performed during the same visit. Correct modifier use remains critical to avoiding bundling edits and ensuring proper adjudication.
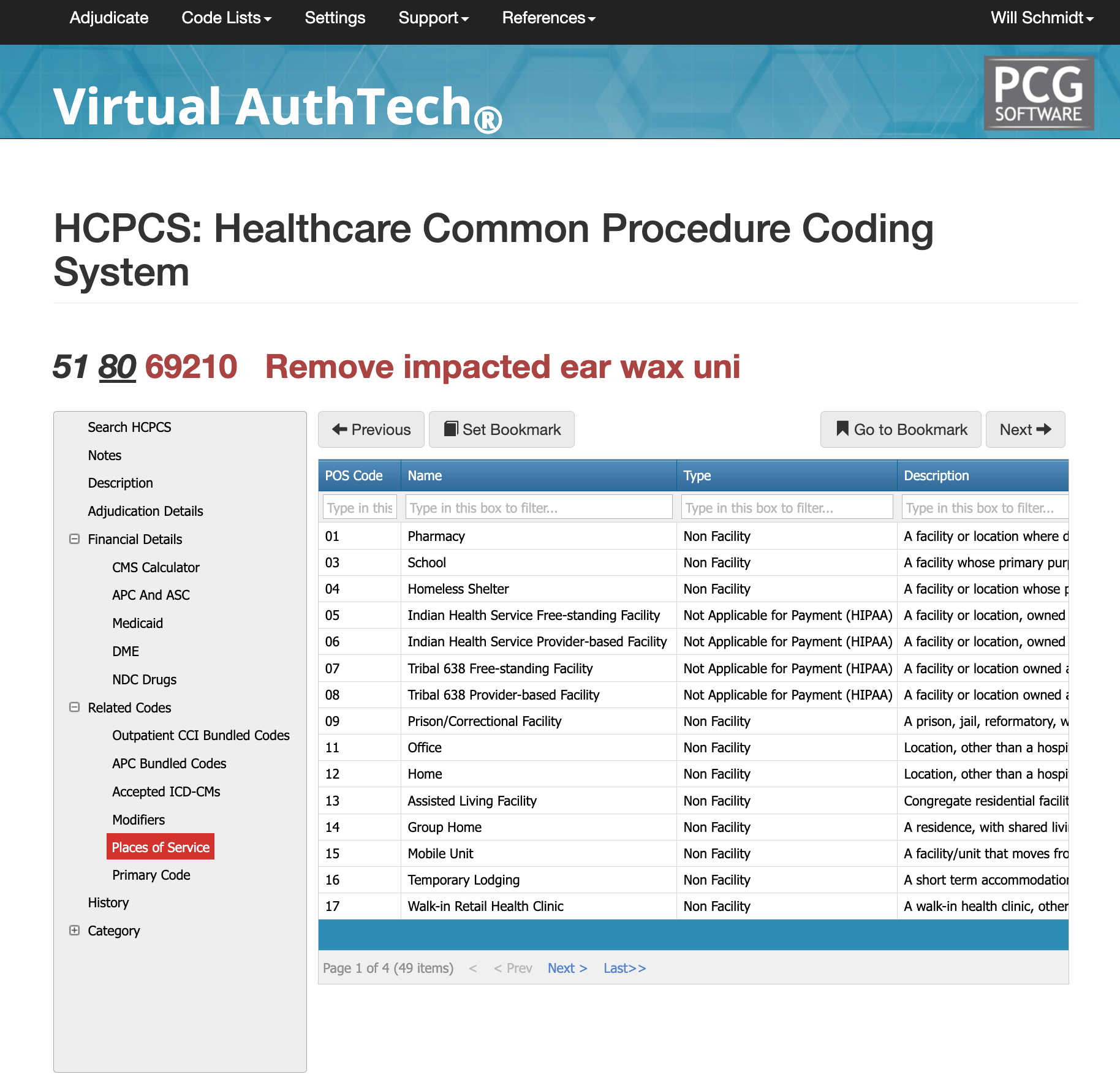
Most Common POS for CPT Code 69210
Cerumen removal requiring instrumentation commonly occurs in physician offices (POS 11), outpatient hospital departments (POS 22), and ASCs (POS 24). It is also frequently performed in urgent care centers (POS 20) and skilled nursing facilities (POS 31), particularly for patients who cannot self-manage symptoms or who require relief from discomfort, obstruction, or infection. Regardless of location, the documentation must clearly support medical necessity, confirm impaction, and describe the instrumentation used to remove the wax.
The Easier Way to Research Codes
For more than 30 years, PCG Software has supported Health Plans, MSOs, IPAs, TPAs, and provider organizations in improving coding accuracy, strengthening compliance, and reducing fraud, waste, and abuse. Our solutions, including Virtual Examiner®, VEWS™, and iVECoder®, are built on decades of payer-side adjudication experience and reflect the same logic used by health plans nationwide. National regulatory guidance, payer policies, compliance standards, and large-scale claims review patterns inform this CPT 69210 analysis.
Toss out the CPT book.
Stop researching articles.
Sign up for iVECoder today!
Subscribe
Only get notifications when a new article has been published
Contact Us
We will get back to you as soon as possible.
Please try again later.
Free Payer Claims Audit
Complete the form, and we'll contact you to schedule an introductory meeting and discuss our FREE 3-year claims audit to identify areas for cost containment and compliance.
Contact Us
We will get back to you as soon as possible.
Please try again later.
About PCG
For over 30 years, PCG Software Inc. has been a leader in AI-powered medical coding solutions, helping Health Plans, MSOs, IPAs, TPAs, and Health Systems save millions annually by reducing costs, fraud, waste, abuse, and improving claims and compliance department efficiencies. Our innovative software solutions include Virtual Examiner® for Payers, VEWS™ for Payers and Billing Software integrations, and iVECoder® for clinics.
Click to share with others